A urogynaecologist female urologist: What Is It? When to See One, What They Do, and What to Anticipate:
In the realm of women’s health, a specialized field focuses on pelvic floor disorders, urinary incontinence, urological stone disease, urological tumor and related conditions.
This area is overseen by a unique medical professional known as a Urogynaecologist/female urologist. While the term may be unfamiliar to many, understanding the role of a female urogynaecologist and knowing when to seek their expertise can significantly impact women’s quality of life.
In this blog post, we explore female Urogynaecologist , shedding light on its intricacies, when to consider consulting one, the scope of their practice, and what patients can expect during their visit.
What is a female Urogynaecologist?
Urogynaecology / female urology represents a distinct subspecialty, focusing on female pelvic medicine and reconstructive surgery.
Urogynaecologists/female urologists are medical professionals specialized in diagnosing and treating pelvic floor conditions such as urinary incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse, where weakened muscles result in the descent of pelvic organs.
The pelvic floor encompasses anatomical structures housing the bladder, reproductive system, and rectum, crucial for maintaining continence and pelvic organ support.
The emergence of Urogynaecology /female urologist as a distinct profession is relatively recent, predating 2011 when various specialists managed pelvic floor disorders independently. Consequently, women often underwent consultations with multiple physicians to address their pelvic health concerns.
In 2011, recognition from the American Board of Medical Specialties established Urogynaecology / female urologist is a standalone field of study, facilitating streamlined care delivery for women with pelvic floor disorders.
This development eliminated the need for women to consult multiple specialists, ensuring comprehensive management of their pelvic health needs within a single medical specialty
What Is the Work of a Urogynaecologist?
Urogynaecologists / female urologist specializes in managing conditions concerning the pelvic floor and bladder, encompassing issues such as overactive bladder, pelvic muscle weakness, reproductive concerns, and urinary or fecal incontinence.
They conduct comprehensive evaluations, including diagnostic assessments, to accurately diagnose and devise treatment plans tailored to individual patient needs.
Treatment strategies are determined based on the specific symptoms experienced and their underlying causes. Common therapeutic modalities employed by Urogynecologists / female urologist include:
Medications:
While not all instances of incontinence necessitate pharmaceutical intervention, certain cases may warrant pharmacological management. Similarly, various pelvic floor disorders may potentially benefit from medication-based treatment modalities.
Injections:
Urogynaecologists/ female urologists utilize “bulking agents” as a therapeutic approach for bladder control and other forms of incontinence. These agents can be administered via injection procedures performed by Urogynecologists/ female urologists under local anesthesia, typically conducted on an outpatient basis or within an office setting.
Vaginal Pessary:
Pessaries, medical devices inserted into the vaginal canal, serve to provide support for pelvic organs in cases of prolapse issues. These devices are constructed from soft materials and are available in various shapes and sizes. Urogynecologists can conduct fitting procedures for pessaries during office consultations. Pessaries are removable for regular cleaning and maintenance.
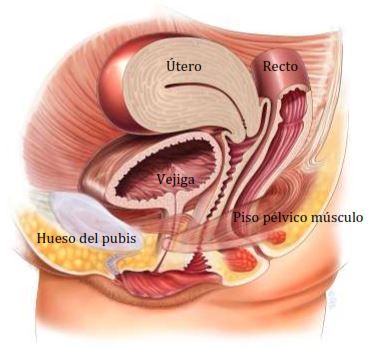
Training To The Pelvic Floor Muscle:
Pelvic floor exercises, commonly referred to as Kegels, can be beneficial for addressing issues such as prolapse. These exercises entail the contraction and relaxation of the muscles within the pelvic floor. While Kegel exercises may offer relief for milder prolapse symptoms, they may not entirely resolve more severe cases..
Surgery:
The female urologist may propose surgical interventions such as:
- Vaginal wall repair
- Bladder installations
- Uterus removal
- Tension free vaginal tape
- Colposuspension
- Ureterorenoscopy with laser
- PCNL
- Laproacopic Nephrectomy
- Flexible ureterorenoscopy with laser
What Conditions Does a Female Urogynaecologist Treat?
Urogynaecologists / female urologist manage a diverse spectrum of pelvic conditions and disorders, which can often be attributed to factors such as obstetric trauma, repetitive heavy lifting, or strenuous physical activities.
Types of the conditions addressed by urogynecologists / female urologist encompass:
- Incontinence of the bladder and rectum
- Urge incontinence
- Overactive Bladder
- Interstitial Cystitis
- Prolapse of the uterus, bladder, or cervix
- Frequent urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- Fistulas
- Renal ,ureteric and vesical stone diseases
- Renal and bladder tumors
Referral to a urogynaecologist / female urologist typically occurs through a primary care physician or other consultant. It is advised to discuss any relevant symptoms during your upcoming appointment with either healthcare provider.
What to Expect at the Female Urogynaecologist?
During your consultation with a urogynaecologist/ female urologist a comprehensive review of your medical history will be conducted, alongside a thorough discussion regarding any symptoms pertaining to kidney, ureter, bladder, Pelvic floor or bladder dysfunction.
The physician will inquire about the extent to which these symptoms affect your daily functioning and quality of life.
Subsequently, a diagnostic evaluation will be performed to ascertain the underlying etiology of your concerns, encompassing an assessment of abdomen, pelvic musculature, ligaments, connective tissue, nervous system integrity, and pelvic organs.
Following the establishment of a diagnosis, collaborative development of a tailored treatment regimen aimed at alleviating your symptoms will be pursued.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Why might I need to see a urogynaecologist/ female urologist ?
You may need to see a urogynaecologist/ female urologist if you experience symptoms related to urinary system ,pelvic floor disorders or bladder dysfunction, such as renal pain, burning in urine, blood in urine ,urinary incontinence, pelvic organ prolapse, or pelvic pain.
What treatments are available for pelvic floor disorders and bladder dysfunction?
Treatment options vary depending on the specific diagnosis and severity of symptoms. They may include lifestyle modifications, pelvic floor exercises (such as Kegels), medication, minimally invasive procedures, or surgery. Your urogynecologist / female urologist will work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to your needs.
What organs are involved in female urology?
The organs involved in urology primarily include the kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra and uterus and ovaries
Conclusions:
In conclusion, urogynaecologists / female urologists play a crucial role in diagnosing and treating urological, pelvic floor disorders and bladder dysfunction, addressing a wide range of symptoms that significantly impact patients’ quality of life.
Through a comprehensive approach that includes a detailed medical history review, thorough physical examinations, and specialized diagnostic procedures, urogynaecologists / female urologists aim to identify the underlying causes of pelvic health issues.
With a focus on personalized treatment plans tailored to each patient’s needs, urogynecologists / female urologists offer a variety of interventions ranging from conservative therapies to minimally invasive procedures and surgical interventions.
By providing compassionate care and support, female urologists empower patients to manage their urologic and pelvic health and improve their overall well-being effectively.
As specialists in this field, female urologists contribute to enhance the understanding and treatment of urological and pelvic floor disorders, ultimately helping patients achieve optimal urological, pelvic health and function.